Developer guide
Get Started¶
To get started, make sure you have a working Go environment and clone the repository:
Prerequisites¶
Before proceeding, please ensure that you have the following dependencies installed:
- Docker or Podman
- Helm
- Aiven CLI (make sure you are logged in)
- jq
- kcat
- base64 (Note: The macOS version does not support the
-w0flag, which may cause some tests to not work properly) - kind
- trunk.io
Create an Aiven authentication token and an Aiven project, you'll need them in the following sections:
AIVEN_TOKEN— your authentication tokenAIVEN_PROJECT_NAME— the name of you Aiven project to run the services in
Optional dependencies:
- k9s — a terminal based UI to interact with our kubernetes clusters
Building¶
The project uses the make build system. To see the available targets, run make help.
Building the operator binary:
Running¶
To run the operator locally, first create a local k8s cluster with kind:
$ kind create cluster --image kindest/node:v1.26.6 --wait 5m
Creating cluster "kind" ...
✓ Ensuring node image (kindest/node:v1.26.6) 🖼
✓ Preparing nodes 📦
✓ Writing configuration 📜
✓ Starting control-plane 🕹️
✓ Installing CNI 🔌
✓ Installing StorageClass 💾
✓ Waiting ≤ 5m0s for control-plane = Ready ⏳
• Ready after 14s 💚
Set kubectl context to "kind-kind"
You can now use your cluster with:
kubectl cluster-info --context kind-kinds
This creates a k8s cluster and points your kubectl to that cluster:
$ kubectl cluster-info --context kind-kind
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://127.0.0.1:58083
CoreDNS is running at https://127.0.0.1:58083/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
Run the operator:
In another terminal window, create a Kubernetes Secret
named aiven-token (use the Aiven authentication token created earlier):
Then, create a manifest for an Aiven PostgreSQL service:
apiVersion: aiven.io/v1alpha1
kind: PostgreSQL
metadata:
name: aiven-devdocs-pg
spec:
# reads the authentication token
authSecretRef:
name: aiven-token
key: token
# stores the PostgreSQL connection information on the specified Secret
connInfoSecretTarget:
name: pg-connection
project: <your-project-name>
cloudName: google-europe-west1
plan: hobbyist
maintenanceWindowDow: friday
maintenanceWindowTime: 23:00:00
userConfig:
pg_version: "15"
...and create the service at Aiven by applying the manifest:
You should see the service be created on Aiven's side using either Aiven Console or Aiven CLI:
$ avn project switch PROJECT_NAME
$ avn service list
SERVICE_NAME SERVICE_TYPE STATE CLOUD_NAME PLAN CREATE_TIME UPDATE_TIME NOTIFICATIONS
================ ============ ========== =================== ======== ==================== ==================== =============
aiven-devdocs-pg pg REBUILDING google-europe-west1 hobbyist 2024-01-01T00:00:00Z 2024-01-01T00:01:00Z
To see the resource on k8s side, use kubectl:
$ kubectl get postgresqls
NAME PROJECT REGION PLAN STATE
aiven-devdocs-pg aiven-sbox-k8s-riski google-europe-west1 hobbyist REBUILDING
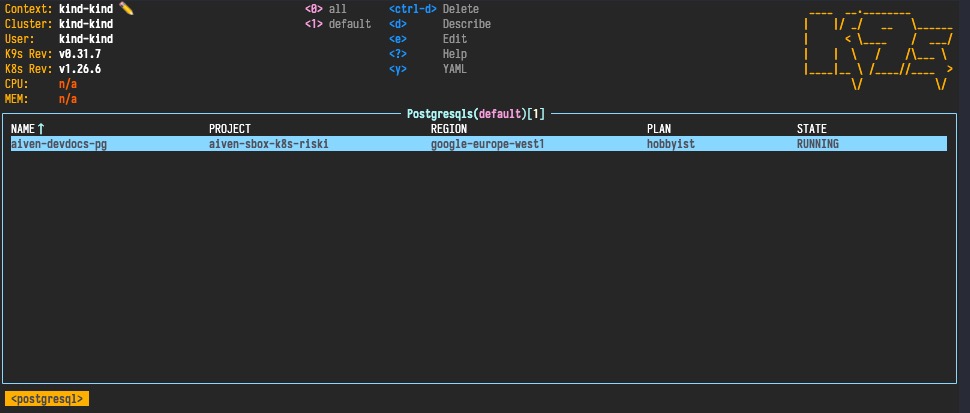
... or by running k9s in another terminal window and type ": postgresqls" to see the provisioned
PostgreSQL resources:
GKE Development Environment¶
For meticulous development and testing, each developer can deploy their own isolated GKE cluster with the Aiven Operator. This environment provides:
- Individual GKE clusters for isolated development
- Artifact repository for built operator images in Google Container Registry (GCR)
- Resource deployment templates for testing of Aiven services
See the GKE Development Setup for detailed instructions on setting up your personal development cluster.
Testing¶
For this section you'll need to set export AIVEN_TOKEN=... and an export AIVEN_PROJECT_NAME=... as well as export ENABLE_WEBHOOKS=false (see Prerequisites).
Note
If you encounter any issues with webhooks, you have the option to disable them by running export ENABLE_WEBOOKS=false
Unit¶
Running all unit tests is possible by running make test. To run a targeted test, use run=TestGrafana make test.
e2e¶
Setup the test environment:
The e2e tests are configured to run against a project called aiven-ci-kubernetes-operator. To run the test against
To remove the kind cluster, simply execute the following command:
Resource generation¶
Please see this page for more information.
Documentation¶
The documentation is written in markdown and generated by mkdocs and mkdocs-material.
To run the documentation live preview:
And open the http://localhost:8000/aiven-operator/ page in your web browser.
The documentation API Reference section is generated automatically from the source code during the documentation deployment. To generate it locally, run the following command:
Generating new resources¶
To create new resources, install operator-sdk with make operator-sdk and run:
# Replace `<VERSION>` with your operator-sdk version.
# Replace `<KIND>` with the new resource type. E.g. "Flink" or "Valkey".
./bin/operator-sdk-<VERSION> create api --version v1alpha1 --kind <KIND> --force
./bin/operator-sdk-<VERSION> create webhook --version v1alpha1 --kind <KIND> --defaulting --programmatic-validation --conversion